Table of Contents
ToggleThe importance of protein
INTRODUCTION
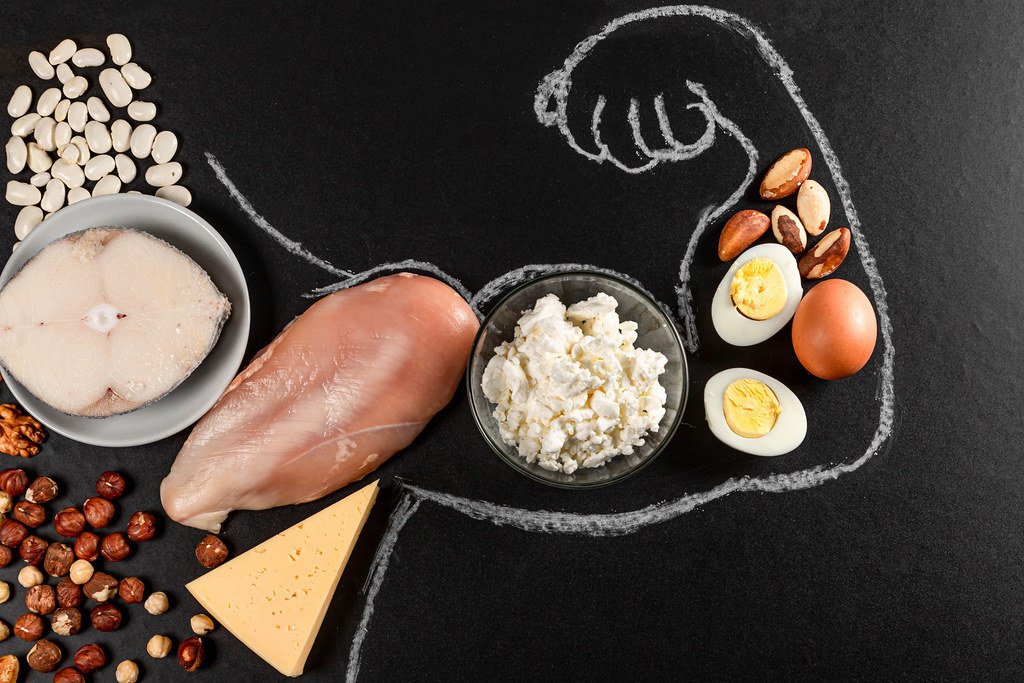
Protein cannot be over-emphasized in the body as it is one of the fundamental life building blocks and is essential to a broad variety of functions. It can build muscle, produce enzymes, support immune health, or perform almost anything else your body needs to continue working. This article will delve deeply into the variety of functions that protein plays in your body, why it is so important, and how you can be sure you get enough of it in your diet.
-
- What is Protein?
What Makes Protein Essential?
- What is Protein?
For the body, protein importance begins at what exactly is protein. Protein, as a macronutrient, consists of amino acids. Those amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Amino acids are used by the body to build new tissues, repair tissues, produce enzymes and hormones, and continue to support the immune system. The body has used 20 different amino acids in producing proteins, but some of which are essential, meaning that the body cannot produce them, and others are non-essential whereby the body can produce on its own.
Role of Protein in the Body
Other than being part of repairing muscles, proteins function in the body as that which includes the production of enzymes to catalyze biochemical reactions, the hormone that regulates metabolism, and even the transport of oxygen through red blood cells. Every one of the billion cells of the body contains protein, making life for itself.
-
- Types of Protein
Full vs. Partial Proteins
- Types of Protein
The major difference between complete and incomplete proteins is what would determine the key to benefit maximization from proteins in the body. Complete proteins consist of the nine amino acids that the body cannot synthesize. Those are: animal-based products including meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy. On the other hand, some, known as incomplete proteins, lack one or more of the essential amino acids. These are commonly found in plant-based sources like beans, lentils, and nuts. Nonetheless, because you can combine different plant-based foods to get all the essential amino acids, there are complete proteins as well.
Sources of Complete Proteins
If you want to increase the weightage of proteins in your body, many of these are best consumed through animal products. Some of the common types of meat are chicken, beef, and pork; seafood includes salmon and tuna. Eggs and dairy items such as milk, cheese, and yogurt also prove good and easy sources of complete proteins.
Completing Incomplete Proteins
The human body is able to obtain enough protein with a vegetarian or vegan diet if various plant-based proteins are combined. Good sources of complete amino acids mixtures would be rice and beans and other foods such as hummus dipped in whole wheat bread, quinoa, and soy-based products such as tofu.
-
- Protein and Muscle Growth
The Role of Protein in Building Muscle
- Protein and Muscle Growth
Probably one of the best-known functions for proteins is in muscle growth. When you are working out, particularly with resistance training or weightlifting, you cause tiny holes in the muscle fibers. Those holes have to be repaired so that there can be muscle growth, and that repair work is facilitated by the use of protein. The amino acids from dietary protein help replace and rebuild tissue in the muscles, making them stronger and better able to cope with stress. It is, therefore, very important for any individual who is planning to construct muscle mass or who at least strives hard to be fit to be intaking protein as well.
Role of Protein in Muscle Repair
The body also requires protein for recovery. Muscles require repair after a workout during the recovery period of the body as well. Protein is essential at this stage of repletion as it helps repair the destroyed tissues, thus enabling the growth back of muscles. Taking protein after a workout will offer the muscles with a sure means of becoming better and stronger as time passes. Taking protein after a short period after a workout would be further helpful in repairing the muscles as the body would have all it needs to recreate the destroyed structure.
Best Time to Take Protein
To provoke muscle growth, a person must consume enough protein each day. Many nutritionists agree that between 1.6 and 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight is the minimum amount needed for athletes and those training with weights. In this way, ensuring that you are actually consuming enough proteins throughout the day-including within 30 minutes post-workout-you can support muscle growth and improve the total benefits from your trainings.
-
- Protein and Immune Function
The Role of Protein in Immune System Health
- Protein and Immune Function
Another important role that protein plays in the body is in the immune system. Proteins help create antibodies, which are vital in fending off pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, and other harmful microorganisms. Whenever the body spots these foreign intruders, the immune system uses those proteins to fight the threat. If the body has insufficient amounts of protein, the immune system will not operate properly, and the body will be susceptible to infections and diseases.
Production of Antibodies by the Protein
Antibodies are proteins designed to selectively eliminate pathogenic bacteria and viruses. These proteins are crucial factors in a body’s defense against infection. In cases where the diet lacks sufficient protein, such inadequate production of antibodies may severely impair the body’s ability to resist infections. For patients whose immune system has been weakened, it will help boost the body’s immunity by raising the absorption of protein.
Protein and White Blood Cells
Besides antibodies, protein is also necessary in white blood cells production needed for the defense of immunity. White blood cells help identify, trap, and destroy pathogens that invade the body from outside. Without enough protein, it would be challenging to produce enough amounts of white blood cells that may lead to increased susceptibility to infection.
-
- Protein in the Production of Hormones
Proteins as Hormones
- Protein in the Production of Hormones
Importance of Protein in the Body Formation of Hormones
This is also where the importance of protein in the body comes out, as it is involved in hormone production. Hormones are chemical substances that signal and regulate a number of activities; among these activities are metabolism, growth, and reproduction. Most of the hormones used in the body are proteins or peptides, and most common examples are insulin, growth hormone, and thyroid hormones. Without protein, the body could not possibly produce these hormones and thereby maintain all body functions.
Protein and Regulation of Insulin
Insulin is a hormone produced from proteins, and it maintains an optimum level of blood sugar within the organism. When carbohydrates are taken, the body decomposes them into glucose, sugar, which then finds its way to the blood. The cells absorb this glucose from the blood, assisted by insulin so that it does not become too concentrated within the blood. Now, the role of proteins in the human body has expanded to ensuring that enough insulin is produced to keep the blood sugar levels at optimal levels for energy and health.
Hormonal Balance and Protein
Maintain a diet with sufficient protein. A diet of adequate protein will allow the body to maintain hormonal balance. The influence will not be limited to insulin, as some other hormones, such as leptin, which controls appetite, and ghrelin, which tells you to eat, are also affected by this. The right protein content in the body will allow the body to maintain enough of what it needs in its bloodstream to metabolize, keep energy up, or even regulate one’s mood.
-
- Protein in Enzyme Function
Enzymes and Role in the Human Body
- Protein in Enzyme Function
Enzymes are proteins that have catalytic properties; they allow biochemical reactions in the body to occur. They include breaking down food during digestion, producing energy, and allowing cellular repair. Enzymes have a hand in virtually all biochemical processes. It just so happens that you cannot have a working body minus the enzymes, which go directly related to importance of protein in the body. By their absence, nutrients in the body will not be broken down, and neither will waste from the body be removed as it should.
Digestive Enzymes
Digestive enzymes are one of the most essential enzymes. They also enable further breakdown of the food items into nutrient particles that the body can absorb and make use of. Here, proteins like amylase, lipase, and protease break down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins respectively. Without these enzymes, digestion will not be proper, and the body will be starved of nutrients and may face some digestive problems.
Production of Enzymes and Protein
The intake of enzymes is directly proportional to protein consumption. Without a proper intake of protein, the body may have a hard time providing the enzyme needed to break down and digest substances further, leading to major malfunctions. Therefore, sufficient protein consumption promotes healthy enzyme production for maintaining optimal bodily functions.
-
- Protein and Skin Health: The Function of Protein in Your Skin Composition
From building blocks of the skin’s structure to firm, smooth, and youthful skin, protein is important for the body, because two of the most important proteins in the skin are collagen and elastin, providing strength, elasticity, and flexibility. Of all the proteins in the body, some 30% of the body’s protein composition is collagen, its main structural protein in the skin, which helps keep it firm, smooth, and youthful. Without enough proteins, the skin loses its elasticity and therefore wrinkles. It becomes saggy at times.
Protein and Skin Renewal
There is skin regeneration, shedding old cells, and creating new ones. Again, the importance of protein in our body appears. The renovation of the skin takes proteins. They provide all the amino acids for the construction of new cells of the skin. They facilitate the growth of new cells in healing processes, and therefore, help in facilitating recovery from injuries and burns by leaving minimal marks.
Protein for Healthy Skin
Some of the ways through which an intake rich diet full of protein may be helpful comprises being included in healthier skin. Due to this intake, you would ensure that your skin structure would be supported due to the production of collagen. Foods with high protein such as eggs, fish, and legumes help a lot in maintaining skin vitality and youthfulness.
-
- Protein for Hair Growth
How Protein Affects Hair Health
- Protein for Hair Growth
Hair is mostly composed of protein; one that the body itself produces. importance of protein in the body can be realized, more so in relation to hair growth. Without sufficient amounts of protein, the hair follicles may weaken and even cause thinning and loss of hair. Adequate intake of protein stimulates hair follicles and encourages hair to grow and become healthier.
Protein and Hair Regrowth
There are even research findings indicating that if you experience hair loss or developing thinner locks, adding more protein to your diet will help. Protein works to rebuild faulty hair follicles and also to enhance the growth of healthy locks. When you incorporate protein-rich food items such as eggs, poultry, and nuts, you give your body building blocks that will help promote hair growth.
Protein and Hair Growth Cycles
Hair grows with cycles, and the only way that hair can support this natural process is from protein. In maximum protein intake, hair follicles continue in the growth phase for longer, resulting in thicker and healthier hair. Therefore, by giving priority to protein in your diet, you support the optimal state of hair health.
-
- Protein and Bone Health
The Function of Protein in Bone Structure
- Protein and Bone Health
The most significant component of bone health is protein. The body’s bones have not just calcium in them but also have a protein content called collagen, which gives elasticity and strength to the bones. Protein is one of the most vital contributors towards body functionality since maintaining bone density has a lot to do with it.
Collagen in the bones also aids in retaining the structure of the bones as well as making them more resistant to breakages.
Bone density seems to drop with age and osteoporosis is one common disorder in which bone breaks due to brittleness. It keeps this at bay by making the bone density high and having strength. Studies show that a diet full of protein will improve the bone with its supporting structure and function. One such food rich in protein, for instance, dairy products, fish, and beans can ensure bone health over time.
Protein for Bone Healing
When the bones become damaged, protein helps in healing. In healing, it assists in rebuilding the tissue in the bones and enhances collagen, which will help make new bone cells. Protein also helps elevate the levels of calcium absorption because calcium is one mineral that plays a significant role in bone health. Therefore, adequate proteins must be consumed when there are fractures of the bones or other bone conditions.
-
- Protein for Digestive Health
Role of Protein in Digestion
- Protein for Digestive Health
The role of protein is not just structural or functional; it also serves a digestive purpose, wherein enzymes-proteins-help break down food into nutrients the body can absorb. Pepsin and trypsin are important digestive enzymes in the process of breaking down protein itself during digestion.
Protein and Gut Health
Apart from the production of enzymes, protein helps keep the guts healthy. Protein aids in repairing the linings of the gastrointestinal tract, hence helping in the successful passage of food within the digestive system. If the linings of the gut get harmed, protein may help restore it and pave the way for digestive system proper functioning.
Protein for Nutrient Absorption
Inorganic protein, which can be used to make digestive enzymes, breaks down the food into smaller molecules. Therefore, once food is well broken down, it helps in nutrient absorption-that the body is able to get necessary nutrients through food. This is possible with enough protein intake, and thus enables the body to realize improved utilization of nutrients and general nutrition status.
-
- How Much Protein Do You Need?
Protein Requirements for Individuals
importance of protein in the body cannot be overstated; however, how much of it we require is another thing. The importance of protein in the body again depend on age, activity level, and also the current health status. The average adult needs about 46-56 grams of protein per day; however, the requirements are different when one is an athlete, pregnant, or an older adult.
Protein and Exercise
Protein needs are higher for individuals who do heavy physical activities regularly. Muscle repair and recovery processes require a higher amount of proteins particularly among active people who are into strength training and endurance sports. Reportedly, the recommended amount of protein for athletes ranges from 1.2 to 2.0 grams per kilogram body weight daily which depends on the intensity of activity.
Protein and Age
The age of a person also has implications on their protein needs. Old people often need more amounts of protein to refrain from losing muscle and to keep their overall health status well.
As we grow older, the metabolism of our body in processing proteins properly decelerates; hence, additional amounts of protein must be taken to keep the muscle mass and bone density high enough.
-
- Signs of Protein Deficiency
What happens when you do not get enough protein?
- Signs of Protein Deficiency
This is an essential part of the body and the absence results in many health disorders; the first sign would be feeling extremely drained as the body cannot even perform simple functions without having sufficient protein. Other signs can include weakness in the muscles, loss of hair, brittle nails, and a weakened immune system.
Critical Protein Deficiency
More severe cases can lead to severe health conditions, like kwashiorkor, which is a common problem in developing countries. Kwashiorkor is characterized by swelling due to edema, stunted growth, and a severely undermined immune system. Although this is rare in developed nations, lack of protein can still help trigger impaired wound healing and increased vulnerability to infections.
Prevention of Protein Deficiency
Normally, to prevent protein deficiency, one must have enough proteins with the right amount in a day. The inclusion of major sources of proteins with every meal can prevent deficiency through dietary consumption. Sometimes, supplementary source intakes in the form of shakes or powders are better if dietary intake is not sufficient for the body.
-
- Protein and Weight Loss
Role of protein in Weight Management
- Protein and Weight Loss
It’s also important for more than just muscle and immune health in the human body. Protein also plays a role in weight management and weight loss. Protein increases the feeling of fullness and tends to help regulate appetite, decreasing calorie intake. Scientific evidence illustrates that higher protein diets can reduce caloric intake and facilitate fat oxidation.
Protein and Metabolism
Other than calorie burnage, the metabolism is enhanced through increased thermic effect of food (TEF), which is a measure of how much energy one requires to digest, absorb, and process food. The thermic effect is a lot higher in case of proteins as compared to carbohydrates and fats as the calories are burnt while processing. And this is where the trick for effective weight loss takes place – increased calorie burn with weight loss.
Protein and Fat Loss
Aside from its role in metabolism, protein plays a role in the retention of lean muscle mass during weight loss. It is no secret that dieting, by definition, results in the loss of both fat and muscle. Consequently, through adequate protein stores, you are more likely to lose fat and retain muscle, giving you a body composition that is lean and healthy.
-
- Protein and Metabolism
How Protein Affects Your Metabolism
- Protein and Metabolism
Proteins help regulate metabolism. Your body will have to expend more energy to digest and process proteins than with fats or carbohydrates. This increased energy expenditure is known as the thermic effect of food (TEF). The higher your protein intake, then so does the boost to your metabolism that helps you to lose weight and burn fat.
Proteins and Muscle Mass
Note here that protein serves to support the maintenance of lean muscle mass, and muscle tissue burns more calories at rest than fat tissue. Therefore, the addition of muscle mass via constant strength training and adequate intake of protein can elevate your resting metabolic rate. The more muscle, the more your body loses calories when resting, and thus the stronger your metabolism overall.
Protein-Rich Foods for an Even Better Metabolism
Metabolic functions will require you to take lots of protein in your diet regularly. Excellent sources of protein include meat, fish, eggs, legumes, and dairy products. These are great for boosting metabolic rate and maintaining body composition.
-
- Protein and Heart Health
The Role of Protein in Heart Function
- Protein and Heart Health
The heart is a vital part of the function that proteins provide besides the muscle and tissues in controlling cholesterol, blood pressure, and health inside the blood vessels. Proteins regulate cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and the general health of the vessel, thus maintaining healthy vascular tissues.
Proteins and Control of Cholesterol
It helps in controlling the cholesterol levels in the body, thereby significantly lowering the LDL cholesterol, also known as “bad” cholesterol. It thus prevents plaque from occurring in arteries, which may lead to a number of cardiovascular diseases, such as atherosclerosis. Some studies have shown that consumption of lean protein sources, for instance fish, along with plant-based proteins, improves the lipid profile and promotes cardiovascular health.
Protein and Blood Pressure
High blood pressure is one of the risk factors most commonly associated with heart disease, and protein help reduce blood pressure by improving the condition of your blood vessels. Intake of proteins high in potassium balances the sodium levels in the body, keeping blood pressure at its optimal rate. On top of that, proteins produce some enzymes, such as ACE, that regulate the condition of the blood pressure.
-
- Protein and Renal Function
How Does Protein Affect the Kidneys?
- Protein and Renal Function
Another important area where the role of protein is vitally important is its relationship with healthy kidney function. The role of the kidneys is to filter wastes out of the blood; the amount of proteins consumed may impact this process. In summary, there is sufficient protein required to keep the kidneys healthy; however, excessive protein consumption can sometimes overburden the kidneys, particularly in individuals who suffer from pre-existing conditions of the kidneys.
Protein Consumption and Kidney Disease
In patients with kidney disease, the regulation of protein consumption is of major importance. A very high intake of protein in the diet makes the filtration process challenging for the kidneys, exacerbating further damage to the kidneys. An appropriate quantity of protein to be taken by someone with kidney disease should be determined through consultation with a health care provider. In patients with kidney disease, yes, protein is essential to protect the kidneys, but its intake must be moderate.
Protein and Kidney Function Preservation
In healthy kidneys, enough protein consumption plays a role in helping maintain the functioning of the kidneys. Protein facilitates the creation of essential metabolites during the process of removing waste products. In addition, since many muscles will be assisting with the overall bodily functions, adequate protein intake is necessary for maintaining muscle mass. Therefore, to maintain proper kidney function, there needs to be an appropriate balancing of protein intake.
-
- Protein and Blood Sugar Regulation
The Role of Protein in Regulating Glucose Levels
- Protein and Blood Sugar Regulation
The body also needs protein to stabilize blood sugar. Proteins ensure that glucose is absorbed slowly in the bloodstream. In the case of diabetes or resistance to insulin, it is imperative to level blood sugar to avoid major surges and crashes.
Protein and Insulin Sensitivity
Insulin is a protein hormone regulating blood sugar levels. Effects on the body’s sensitivity to insulin exist from dietary protein. Improved insulin sensitivity on the part of the rich diet in protein means the proper body usage of insulin in the control of blood sugar levels, which will be instrumental in preventing or managing type 2 diabetes and lowering the risk of developing it.
Role of Protein in Preventing Blood Sugar Spikes
Consuming proteins together with carbohydrates delays the speed at which glucose is absorbed into the body. This makes protein an integral component of a balanced meal plan for people desirous of blood sugar control and prevention of metabolic disorders.
-
- Protein and Mental Health
Role of Protein in Brain Function
- Protein and Mental Health
Another reason why protein is important in the body has to do with its impact on mental health. Protein makes sure that there is a neurotransmitter formation in the brain. Neurotransmitters are chemicals, helping to facilitate signals across the brain; they deal with mood, memory, and how one functions mentally. Amino acids from protein produce these neurotransmitters, hence protein plays a major role in maintaining mental clarity and emotional stability.
Protein and Mood
The absence of protein from the diet causes neurotransmitter imbalance, which has an impact on mood. In a case where tryptophan amino acid, contained in highly protein-requisite foods such as turkey, is insufficient, then serotonin, a neurotransmitter that calms moods and feelings of well-being, is in limited quantities. The right amount of protein production ensures the correct production of serotonin and other neurotransmitters that regulate mood stabilization.
Protein and Brain Function
Protein is involved in cognitive function. In other words, concentration and memory all need proteins to perform effectively. Protein deficiency is diagnosed by symptoms such as brain fog, inability to concentrate, and issues with memory. Sufficiency of its consumption in the diet ensures optimal cognitive health as well as optimum brain function. In more detail, the brain’s ability to improve the daily output of productivity and mental performance.
-
- Protein and Hormonal Health
How Protein Supports the Manufacture of Hormones
- Protein and Hormonal Health
Hormones control almost everything in the body-from growth to metabolism to mood. Because hormones also often come in the form of proteins or peptides, protein is therefore the most vital chemical needed by the body in order to produce hormones; thus, without sufficient amounts of protein, the body will fail to produce the needed hormones for optimal health.
Protein and Thyroid Function
The thyroid hormones regulate metabolism, energy, and growth in the body. With no proteins, one might end up with a deficient thyroid that causes a metabolic and energy imbalance. Therefore, having enough proteins is essential because it will help support thyroid hormone production; hence, a healthy metabolic rate and energy will be preserved.
Protein and Reproductive Health
Protein also plays an important role in reproductive health. Some of the functions include production of sex hormones such as estrogen and testosterone. In a woman, these hormones regulate the menstrual cycle, whereas, in a man, they control the production of sperms. This synthesis of the above-mentioned hormones is required for the optimal functioning of the reproductive system in the human body.
-
- Protein and Weight Management
Role of Protein in Appetite Regulation
- Protein and Weight Management
Protein is essential for weight control because proteins control hunger and restrain overeating. Because they increase feelings of fullness and decrease hunger, protein-containing foods have the tendency to minimize calorie intake. This makes a nutrient that is pretty crucial for those looking at keeping up a healthy body weight and reducing body fats.
Protein and Satiety
High Protein Promotes Hormonal Responses That Reduce Hunger: Protein increases levels of hormones that demonstrate fullness, such as peptide YY and GLP-1. These hormones enable the brain to understand its state of satisfaction, thereby lowering overall food intake. Inclusion of high levels of protein in one’s diet helps increase feelings of fullness and eliminates the behavior of unhealthy snacking, which is a facilitator of weight gain.
Protein and Body Fat Loss
In addition to its impact on satiety, protein also maintains lean mass during weight loss. Losing weight and especially in caloric restriction, protein helps assure that most of the weight is lost as fat, rather than as muscle. In doing so, it supports greater metabolism, which is beneficial for better long-term weight retention as well as fat loss.
-
- Protein and Bone Density
The Role of Protein in Bone Health
- Protein and Bone Density
Protein also assists in keeping your body with enhanced density and strength of the bones. The protein type that is found in most structural components of the human body is collagen. Essential structures include bones, tendons, and cartilage. Protein assists in maintaining the structure of bones, thereby providing them with the strength and reduced susceptibility to fractures.
Absorption of Calcium and Protein
While calcium is necessary for healthy bones, proteins facilitate the absorption and utilization of calcium by the body. Protein also assists in the synthesis of osteocalcin-a protein that facilitates calcium binding to bone. For these reasons, a diet with adequate portions of both protein and calcium may be considered good for bone health, as it may help densify the bones.
Proteins and Bone Repair
Protein plays a very important role when bones are hurt. This plays an important role in stimulating regeneration in bone cells, and it promotes the generation of new tissue in bones. Sufficient protein consumption can speed up the healing of broken bones and strengthen your bones as a whole.
-
- Protein and Cellular Repair
The Role of Protein in Cell Regeneration
- Protein and Cellular Repair
The body also needs protein for the cellular repair process. All cells in the body are made up of proteins, and protein is required for regenerating and rebuilding cells. It might be a damaged skin cell, muscle cell, or red blood cell, in which case protein will rebuild and restore it to its original work.
Protein and Healing of Tissues
The body needs a high amount of protein after suffering any form of injury or surgery in order to repair damaged tissues. Protein will facilitate the generation of new tissue and speed up healing processes. The reason why protein is emphasized as part of recovery plans of athletes, surgery, wounds, or injuries is that it aids in rebuilding new tissue hence fastening healing processes.
Protein and Organ Health
There are components in the organs, such as the liver, kidneys, and heart, which require proteins to regenerate and repair them. Organs continuously regenerate and repair themselves through a mechanism that requires protein for its repair process. This will assure appropriate intake of protein can repair and enable functionality of vital organs, so tend to ensure health and longevity.
Well, let’s summarize that for you. . .
-
- Protein and Immune Health
How Protein Supports the Immune System
- Protein and Immune Health
The function of the immune brings greater importance to proteins in the body. Production of immune cells and antibodies, which aid in the defense of the body from any harmful pathogens, involves proteins. White blood cells are very crucial for your body in fighting off infections, and mainly these blood cells comprise proteins. Sufficient protein intake facilitates your body to produce enough immune cells to protect against infections caused by bacteria, viruses, and other aggressive pathogens.
Protein and Antibody Production
You must have already learned that antibodies are proteins which can identify and neutralize foreign invaders, such as bacteria, viruses, and toxins. Your body needs sufficient protein for producing these antibodies and to facilitate an effective immune response. A dearth of protein can lead to a depressed immune system, leaving you vulnerable to infection.
Protein and Recovery of the Immunity System
After an illness or infection, the body requires protein to regain its strength and rebuild. Protein has a significant role in the restoration of immune cells and tissues so that the body can regain its former strength after an illness. This makes the role of protein crucial in maintenance towards long-term health, particularly among individuals who are under recovery from surgical interventions, injury, or diseases.
-
- Protein and Mood Stability
The Role of Protein in Mood Regulation
- Protein and Mood Stability
Beyond physical needs, protein is crucial to the mental aspect of human health, including moods. The fundamental element that these acids are derived from is protein and are required in the synthesis of neurotransmitters that include serotonin and dopamine in making neurotransmitters as norepinephrine, which regulate mood. These neurotransmitters promote happy feelings, focus, and relaxation.
Protein and Neurotransmitter Synthesis
Some amino acids from dietary protein become neurotransmitters. Tryptophan is converted into serotonin, considered the “feel-good” neurotransmitter because of the mood elevating properties of serotonin. Tyrosine produces both dopamine and norepinephrine, which regulate mood and mental acuity. A diet that does not supply enough protein will result in an imbalance that contributes to mood swings, anxiety, and depression.
Protein and Stress Management
During stress, the body uses protein for the production of hormones associated with stress reactions and for modulation of the body’s response to stress. Stabilization of blood sugar can also prevent stress-induced spiking or crashing of blood sugar. Also, proper protein intake can regulate the level of cortisol, a hormone associated with stress responses.
-
- Protein and Pregnancy Health
Why Protein Matters During Pregnancy
- Protein and Pregnancy Health
Protein during Pregnancy
Protein is essential during pregnancy because the baby needs it to develop and grow, and it is also needed to keep a mother healthy. The formation of proteins helps in the development of baby’s organs, muscles, and tissues. Lastly, protein serves as a significant means of helping a placenta to remain healthy and its nutrient needs delivered to the baby.
Proteins for Maternal Health
A pregnant woman requires more protein to help produce the baby and prevent the mother from losing muscle mass. Ensuring adequate levels of protein helps maintain a healthy mother’s immune system and hormone production. This also plays critical roles with respect to the regulation of blood pressure and fluid balances, which assume vital importance in pregnancy.
Protein and Fetal Development
Protein is vital in the development process of a baby, particularly during the last two trimesters when baby growth spurt. Aiding adequate protein provisions ensure healthy production of cells, tissues, and other organs in the fetus. Protein also helps to supply nutrients needed to build the baby’s brain and muscles.
-
- Protein and Muscle Repair
The Role of Protein in Recovery
- Protein and Muscle Repair
This is one of the beneficial effects of proteins, its role in muscle repair and building. After rigorous exercise, muscle fibers sustain injuries and microscopic deterioration. Healing these fibers and, above all, making them stronger must be done through protein consumption, and that is why athletes and bodybuilders take such high interest in protein intake to help them out in the healing process and growth of muscles.
Protein and Exercise Performance
The body uses protein for reasons more than just the repair of muscles. Protein maintains muscle and energy during exercise performance. When exercise goes longer than necessary, prolonged exercise, the body breaks down the use of protein to supply its energy, as well as support the action of the muscles. Adequate protein intake helps build performance and endurance.
Protein and Preventing Muscle Loss
As humans age, they have natural losses in muscle mass. Protein intake is important to prevent the process of sarcopenia. A high-protein intake prevents older adults from losing strength, mobility, and function in their muscles. For an individual on a weight-loss diet, protein helps the body maintain muscle mass during the weight loss period to limit its loss behind fat losses.
-
- Protein and Healthy Aging
The Role of Protein for the Elderly
- Protein and Healthy Aging
Aging makes it hard to remain healthy and active. Proteins play a very important role in the body during aging because they prevent losing muscles, weakening bones, and general frailty. Protein intake is essential for healthy aging individuals in terms of maintaining independence, mobility, and quality life.
Proteins and Osteoporosis in the Elderly
Protein is quite effective in maintaining the bones among the elderly. As aging progresses, the capability of the body to absorb calcium becomes weakened, while protein consumption can also aid in the retention of bone density. Another important function of protein is in the collagen from which many bones, joints, and tissues are made of. Adequate intake of proteins by the aged population will prevent osteoporosis and fractures.
Proteins and Muscle Mass in the Elderly
Sarcopenia is the gradual loss of muscle mass and strength, which is common in geriatric patients. Proper intake of protein with consistent exercise practice is fundamental to the prevention of sarcopenia. Protein-rich diets help older adults retain their muscular strength and prevent this effect associated with old age.
-
- Protein and Hormonal Balance
How Protein Supports Hormone Production
- Protein and Hormonal Balance
Protein is central to the maintenance of hormonal balance within the body. Most hormones, such as insulin, growth hormone, and sex hormones, are synthesized from proteins or amino acids. These hormones play an important role in the regulation of metabolism and reproduction. This importance of protein is well explained in relation to the condition of hormone regulation, where low intake of protein eventually results in the destabilization of the equilibria of hormones.
Protein and Glucose Level
It is interesting that hormones like insulin, which regulate blood sugars, are directly influenced by the intake of proteins. Adequate protein intakes ensure that the body can produce sufficient amounts of insulin as required to keep the blood sugar levels within a stable range. This aspect is significantly important in individuals with insulin resistance and diabetes.
Protein and Stress Hormones
Whenever it is under physical or emotional stress the body produces hormones like cortisol. Protein is involved in regulation of production of hormones such as cortisol associated with stress. Adequate protein intake maintains the body’s response to stress under balanced and controlled mechanisms .
-
- Protein and Cellular Health
The Role of Protein in Cell Function
- Protein and Cellular Health
Cells use protein to execute a variety of functions, including growth, division, and repair. This matters at the cellular level because the body’s need for protein mirrors the body’s almost endless cellular functions-from DNA repair to energy production.
Protein and Immune Cells
Protein is present in all immune cells, like white blood cells. These cells are very important for fighting infections and to beat an invading organism. It helps the production and action of cells that are crucial for maintaining a strong immune response in the body.
Protein and Cellular Regeneration
Cellular regeneration is the constant generation of new cells with replacement of older, damaged cells in the body. Protein is required for cell regeneration so that tissues are renewed and repaired continuously. This would ensure the general state and sustain tissue repair following injuries or surgery.
-
- Protein and Athletic Performance
Protein and Muscle Building
- Protein and Athletic Performance
Athletes and bodybuilders know how much protein is need for the body, especially when it comes to the muscle building. Protein provides necessary amino acids which facilitate the repair and growth of fiber strands of muscles stressed by exercise. This process is necessary in building strength, power, and endurance.
Protein and Recovery Time
Recovery is also not to be forgotten while training. Protein helps repair muscles and decrease soreness after exercise, keeping the recovery time at a minimum. Train harder, train more often means taking in enough protein will definitely allow athletes to perform well and better on the whole.
Protein and Enhancement of Performance
It helps in recovery and also increases muscle mass and strength, hence improving athletic performance. If one consumes the appropriate level of protein intake before exercise, and during and even after the exercise, an athlete will achieve his or her fitness goals.
Conclusion
Protein is important in the body; the above advantages justify it. From building muscles to repairing tissues, regulating hormones, and supporting the brain, protein supports all aspects of health. And regardless of whether you are an athlete, an aging adult, or just someone wanting to remain as healthy as possible, adequate protein intake is key.
So, understand the key roles that proteins play in your body and incorporate those protein-rich foods into your diet, which will help you optimize your health and well-being. After all, when you’re talking about protein, you’re talking about one of the most powerful nutrients for maintaining a strong, healthy body and mind.